Steam Gasification Plant Designed

for Efficient Conversion of Various
Biomass into Fuel & Chemical Feedstock
TIGAR® gasifies biomass resources to produce syngas (synthetic gas: hydrogen, carbon monoxide and other usable gases), which are utilized for various applications such as chemical feedstock and power generation fuel.
TIGAR® consists of the bubbling fluidized bed (BFB) where biomass resources are converted to syngas by the gasification reaction and the circulating fluidized bed (CFB) where unreacted biomass resources are completely combusted. In this circulatory system, bed materials (sand) are circulating to supply heat with BFB and enhance gasification reaction (see Fig. 1).
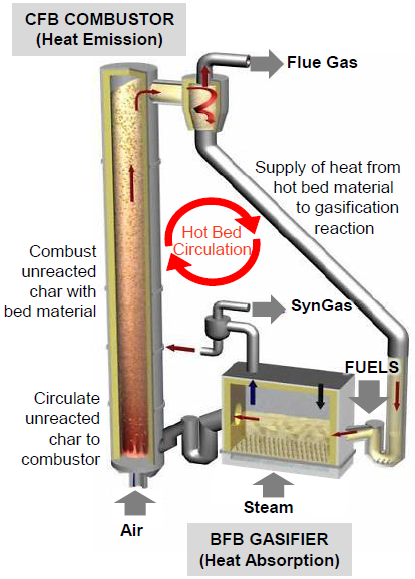 Fig. 1 The main feature of TIGAR®
Fig. 1 The main feature of TIGAR®
Major Features and Advantages
- Safer and Easier O&M
・Relatively low temperature & Low pressure
- Enables a safer and easier operation.
- Low-cost plant manufacturing and operational maintenance.
- The technical similarity to the CFB boiler
・Plant components and operation process are similar to the CFB boiler.
- Vairous options for gasification feedstock
・Applicability to various feedstocks
- Wood chip/pellet, bagasse, bark, Lignite, sub-bituminous coal and other biomass can be treated.
 Fig. 2 The example of gasification feedstock
Fig. 2 The example of gasification feedstock
・Co-gasification of lignite and biomass
- Lignite and biomass can be gasified at the same time.
・Easy switch over to any feedstock
- Gasification feedstocks are smoothly switchable during continuous operation.
・The input to gasifier with a coarse grain size of the feedstock
- A coarse grain size of lignite (Approx. 10mm, moisture content=60%, with pre-treatment) is permissible to feed.
- Syngas with Rich-H2
・100% steam gasification system
- Hydrogen accounts for a large percentage of syngas.
- N2 contamination is significantly reduced compared to the entrained bed.
Technology Data
Possible applications
The “TIGAR®” technology facilitates the realization of de-carbonized society by promoting the utilization of biomass resources in developing countries. “TIGAR®” gasifies unutilized biomass resources and produce syngas which mainly consists of H2. Syngas can be utilized for several kinds of application such as a substitute for fossil fuel, electricity generation and chemical feedstock and so on (see Fig. 3).
By converting unutilized resources into a high-value product, “TIGAR®” reduce a large volume of CO2 emission and provide a new clean energy solution.
 Fig. 3 The scheme of TIGAR® application
Fig. 3 The scheme of TIGAR® application
Competitive advantage
1. Reasonable plant cost with moderate operational conditions
Competitive gasification technology like entrained bed gasifier is required to operate under the condition with high temperature and high pressure, consequently, lead to high specification manufacturing cost.
On the other hand, “TIGAR®” can be operated on atmospheric pressure and relatively lower temperature and hence the gasifier plant can be built with readily available equipment.
2. High purity syngas derived from separated structure
Generally, as is the case with many other gasifiers, the heat required for the gasification process is supplied by the combustion of a part of the feedstock in the gasifier.
For this purpose, oxygen generated by an expensive Air Separation Unit (ASU) is injected into the gasifier as a gasification agent. In contrast, TIGAR® uses heated sand circulating from the combustor to derive the required heat for gasification while steam is used as a gasification agent in the gasifier (see Fig. 4).
Hence, oxygen is not necessary for the gasification reaction. Additionally, air is fed into the combustor in order to provide combustion heat. Since the combustor and gasifier are separated from each other and only heated sand circulates into the gasifier, flue gas does not mix with syngas. It is thus possible to obtain syngas with high calorific value, which is also suitable for chemical raw materials.
 Fig. 4 Circulation flow of bed materials (heated sand)
Fig. 4 Circulation flow of bed materials (heated sand)
Performance
1. High calorific syngas with rich contents of H2
“TIGAR®” enables gasification process with 100% of steam, thus produce hydrogen-rich syngas. (For brown coal gasification, the proportion of hydrogen in the syngas is about 50%).
In addition, since the gasifier and the combustor are separated, the syngas and the combustion exhaust gas are completely separated. Thereby, it is possible to produce syngas having a high calorific value with little mixing of nitrogen, and that has been verified in the 50TPD demonstration plant in Indonesia.
2. Reduction of CO2
One of the main applications of syngas is to produce hydrogen which is used as chemical feedstock. Hydrogen is generally produced by fossil fuel such like natural gas.
The amount of CO2 emission of hydrogen plant of is as following;
*for producing 10,000Nm3-H2/hr
using natural gas : Approx.10 ton/hr
using biomass with TIGAR : Approx. 2ton/hr
Technical maturity / Past record of introduction
IHI Corporation started development of TIGAR® in 2004. After conducting the labo-scale experiment and the test operation in the domestic pilot plant with a coal feeding rate of 6-50 t/d, IHI demonstrated the TIGAR® 100 t/d plant in Indonesia, where low rank coals and biomass were abundant and the development of technology for their utilization was actively supported. In this project, the feasibility of its scaled-up design and biomass feedstock were successfully confirmed (see Fig. 5).
 Fig. 5 Development and history of TIGAR®
Fig. 5 Development and history of TIGAR®
In 2017, “TIGAR®” technology has completed nearly 6,000 hours of demonstration operation in Indonesia and is in a commercial ready state. Since feedback of the demonstration operation results to the commercial machine design has already been completed, it is possible to provide a commercial machine with stable technology.
 Fig. 6 TIGAR® demonstration plant in Indonesia
Fig. 6 TIGAR® demonstration plant in Indonesia
Information on patent related to this technology
2005-41959
Company Data
| Name | IHI Corporation |
| Address | TOYOSU IHI BUILDING., 1-1, Toyosu 3-chome, Koto-ku, Tokyo 135-8710, Japan |
| Capital | 107.1 billion yen (as of March 31, 2018) |
| Contact person |
Mr. Daichi Nakahara |
| Number of employees | 29,706 (as of March 31, 2018) |
| Date of company foundation | December 5, 1853 |
| Type of business | Heavy industry manufacturer |
Corporate website: https://www.ihi.co.jp/en/
International operation
| Number of employees for international operation |
66 (as of January 2019) | |
|
Overseas offices |
City, Country | Name of Company (if applicable) |
| Singapore | Singapore Office | |
| France | Paris Office | |
| Italy | Rome Office | |
| Algeria | Algeria Office | |
| Russia | Moscow Office | |
| Turkey | Instanbul Office | |
| India | New Delhi Office | |
| Thailand | Bangkok Office | |
| Vietnam | Hanoi Office | |
| Malaysia | Kuala Lumpur Office | |
| Indonesia | Jakarta Office | |
| China | Beijing Office | |
| Taiwan | Taipei Office | |
| Korea | Seoul Office | |
| United Arab Emirates | Dubai Office | |
| And 147-overseas subsidaries | ||
Modality of business transaction
Partnership
IHI deliver the gasifier plant under cooperation with a local partner on plant construction, operation and maintenance.
Export of product
IHI is responsible for engineering, procurement and construction.
Attachments
Schematic illustration of the technology
Press Release, March 2, 2015
https://www.ihi.co.jp/en/all_news/2014/resources_energy_environment/2015-3-02/index.html
IHI Engineering Review, Vol. 50, No.1, 2017
https://www.ihi.co.jp/var/ezwebin_site/storage/original/application/25ca562073dd485aeee3cb0c6697ac15.pdf
Contact Person(s)
*Please mention that you saw UNIDO's website when making the first contact with the company.
Registered Category
- Energy Technologies : Renewable energy / Utilization of unused resources